Risk Register Excel Template
Introduction
A risk register is a fundamental tool in project management that helps identify, evaluate, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle. It is an essential document that enables project managers to proactively address potential issues and develop strategies to mitigate or minimize the impact of these risks.
What is a Risk Register? in Project Management?
A Risk Register, often called a Risk Log, is a document or tool used in project management to identify, assess, and manage risks. It is an organized and detailed record of potential risks that may impact the project's success.
The purpose of a Risk Register is to provide a centralized repository for all identified risks, associated impacts, likelihoods, and mitigating actions. It helps project managers and stakeholders understand and prioritize risks, allowing them to develop appropriate response strategies.
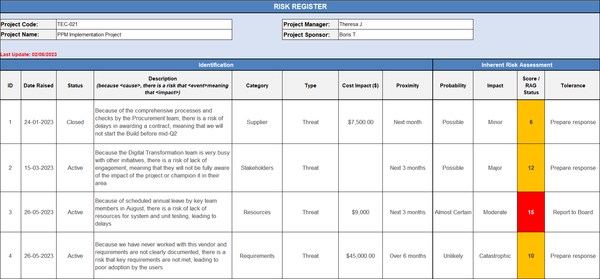
A Typical Risk Register includes The Following Information:
- Risk description: A detailed explanation of the risk event or situation.
- Category: The specific area or aspect of the project to which the risk pertains, such as schedule, cost, quality, or safety.
- Impact: The potential consequences or effects of the risk on the project if it occurs, such as delays, increased costs, or compromised quality.
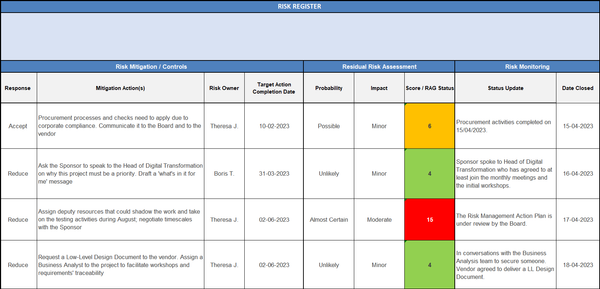
- Risk owner: The individual or team responsible for monitoring and managing the risk.
- Risk response: The planned actions or strategies to address the identified risk, including prevention, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance.
- Contingency plan: A backup plan or alternative course of action to be implemented if the risk occurs.
- Status: The status or stage of the risk, indicating whether it is still open or has been resolved or closed.
- Priority: The level of importance or significance assigned to the risk, often based on its likelihood and impact.
What Are The Key Components Of A Risk Register?
- Identification: This component involves identifying and listing all potential risks that may impact the project's objectives. It includes gathering input from stakeholders, team members, historical data, and other sources to ensure a comprehensive list of risks is captured. Each risk should be described in clear and concise terms to facilitate understanding.
- Inherent Risk Assessment: After identifying the risks, the next step is to assess their inherent risk, which means evaluating the risks without considering any risk mitigation measures. Inherent risk assessment helps in understanding the magnitude of the risks and their potential impact on the project if no action is taken to address them.
- Risk Mitigation/Controls: Risk responses or mitigation strategies are developed to reduce the probability and impact of identified risks in this component. Each risk should have corresponding control measures that explain how the risk will be managed or addressed. These controls can include risk avoidance, risk transfer, risk acceptance, or risk reduction through specific actions.
- Residual Risk Assessment: Once mitigation measures are applied, the risks are reassessed to determine their residual risk. Residual risk is the risk that remains after implementing the mitigation strategies. It helps understand the controls' effectiveness and whether additional measures are needed.
- Risk Monitoring: Risk monitoring involves regularly tracking and reviewing identified risks and their corresponding controls throughout the project's lifecycle. It includes updating the risk register as new risks arise, evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls, and ensuring that the project team remains vigilant to potential changes in risk circumstances.
What Is The Process Of Creating a Risk Register?
The Process of Creating a Risk Register
1. Risk Identification
In this step, the project team and relevant stakeholders collaborate to identify potential risks that may impact the project's objectives.
Conduct brainstorming sessions, review historical data from similar projects, and use risk analysis techniques like SWOT analysis to identify risks.
Document each identified risk in the risk register, clearly and concisely describing the risk event.
2. Risk Assessment
- Once the risks are identified, the next step is to assess and evaluate each risk's likelihood and potential impact on the project's success.
- Use qualitative and quantitative risk assessment methods to assign each risk a probability and impact rating.
- Record the likelihood and impact ratings in the risk register.
3.Risk Prioritization
- Prioritize the identified risks based on their likelihood and impact ratings. This helps in focusing on the most critical risks that require immediate attention.
- Consider using risk matrices or other prioritization techniques to rank the risks.
- Assign a priority level (e.g., high, medium, low) to each risk and update the risk register accordingly.
4. Risk Owner Assignment
- For each identified risk, designate a risk owner responsible for managing and monitoring that specific risk.
- The risk owner should have the expertise and authority to implement risk mitigation strategies.
- Specify the risk owner in the risk register.
5. Risk Response Planning
- Work with the risk owner to develop appropriate risk response plans for high-priority risks.
- Mitigate, transfer, accept, or avoid the identified risks based on the project's risk tolerance and available resources.
- Record the planned risk responses in the risk register.
6. Risk Monitoring and Review
- Regularly review and update the risk register throughout the project's lifecycle.
- Monitor the progress of risk response plans and assess whether they effectively manage the identified risks.
- Capture any new risks that may emerge during the project and add them to the risk register.
7. Communication and Reporting
- Ensure effective communication of risk-related information to all stakeholders involved in the project.
- Use the risk register as a central document for sharing risk status updates and changes.
- Provide regular risk reports to project sponsors and stakeholders to inform them of the project's risk profile.
Benefits of Using a Risk Register
- Proactive Risk Management: A risk register enables project managers and teams to identify potential risks before they escalate into issues proactively. By capturing and documenting risks early in the project, teams can develop appropriate response plans and mitigate potential negative impacts. Proactive risk management minimizes the likelihood of surprises and helps the project stay on track.
- Improved Decision-Making: The risk register provides stakeholders with valuable insights into the project's risk profile and potential areas of concern. With this information, decision-makers can make informed choices about project priorities, resource allocation, and risk response strategies. The risk register is a reference point for risk-related discussions, guiding stakeholders in making prudent decisions.
- Enhanced Communication: The risk register is a central repository of risk-related information, fostering transparent and effective communication among project teams and stakeholders. It facilitates risk discussions, allowing stakeholders to understand the project's risk landscape and collaborate on risk response plans. Enhanced communication leads to better alignment among team members and increased stakeholder engagement.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Maintaining a risk register demonstrates that the project team diligently identifies and addresses potential risks. Stakeholders gain confidence in the project's management, knowing risks are monitored and managed. A transparent approach to risk management fosters trust and strengthens relationships with project sponsors and stakeholders.
- Resource Optimization: With a risk register, project teams can allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on high-priority risks that significantly impact the project. Resources can be directed towards risk response strategies, ensuring they are used effectively to safeguard project objectives. Avoiding or mitigating risks can prevent resource wastage and costly rework.
- Early Issue Identification: Risks in the register that materialize into issues can be identified and addressed promptly. Early issue identification allows teams to respond promptly and implement corrective actions to prevent further negative impacts on the project. This proactive approach minimizes the potential escalation of issues into significant problems.
- Project Resilience: A comprehensive risk register enhances the project's ability to adapt to unforeseen events and changes in the project environment. It empowers the project team to be agile in responding to emerging risks and uncertainties, maintaining project resilience. Resilience enables the project to recover quickly from setbacks and progress towards completion.
Conclusion :
We began by defining the risk register and highlighting its purpose in capturing and documenting project risks. We then discussed the key components of a risk register, such as risk descriptions, likelihood, impact, and risk owners, providing a comprehensive understanding of its contents.
In conclusion, we reiterated the significance of risk management and the pivotal role of the risk register in effective project planning and execution. By implementing a risk register and adhering to best practices, project managers can foster a risk-aware culture and increase the likelihood of project success.



